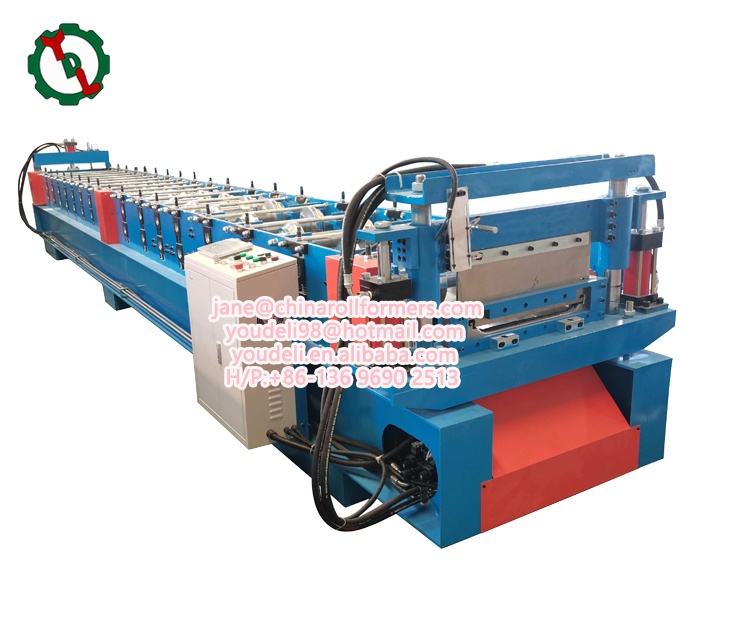
Introduction:
In the realm of metal fabrication, the corrugated roll forming machine stands as a technological marvel, seamlessly transforming flat metal sheets into intricately corrugated profiles. Understanding the intricate workings of this machine and the pivotal components involved is paramount for professionals and enthusiasts alike. This article delves into the operational dynamics of a corrugating roll forming machine, shedding light on the key components that orchestrate the process with precision.

I. Overview of Corrugated Roll Forming:
At its core, a corrugated roll forming machine is designed to shape continuous lengths of metal coils into corrugated profiles. This process involves a series of precisely orchestrated steps that contribute to the creation of durable, versatile, and aesthetically pleasing corrugated sheets used in various industries such as construction, packaging, and automotive.
II. Key Components and Their Functions:
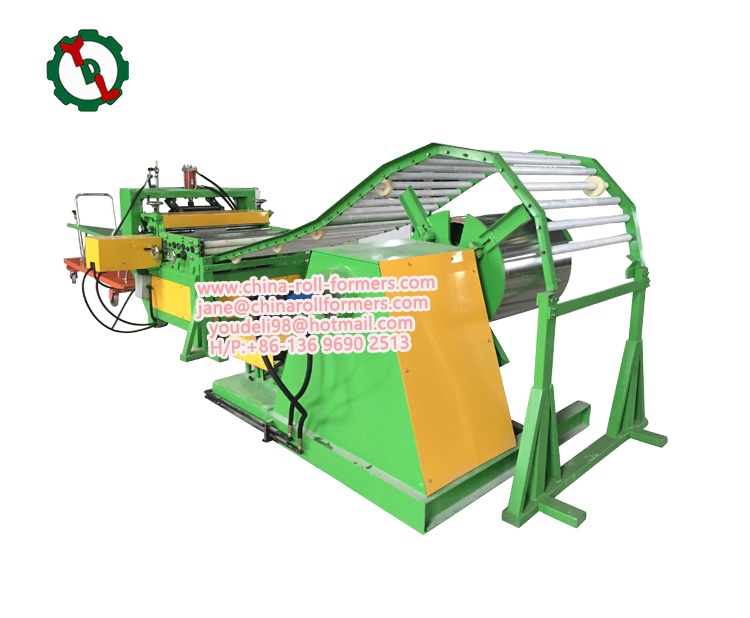
- Uncoiler:
Function: The uncoiler serves as the starting point of the process by holding and gradually releasing the metal coil. This controlled release ensures a steady feed of material into the roll forming machine.
- Leveler:
Function: Metal coils often arrive with variations in flatness. The leveler corrects these imperfections by applying consistent pressure, ensuring a uniformly flat surface for the subsequent forming stages.
- Servo Feeder:
Function: The servo feeder precisely measures and feeds the metal coil into the machine, controlling the length of material to be corrugated. This component plays a critical role in achieving accurate and uniform corrugation.
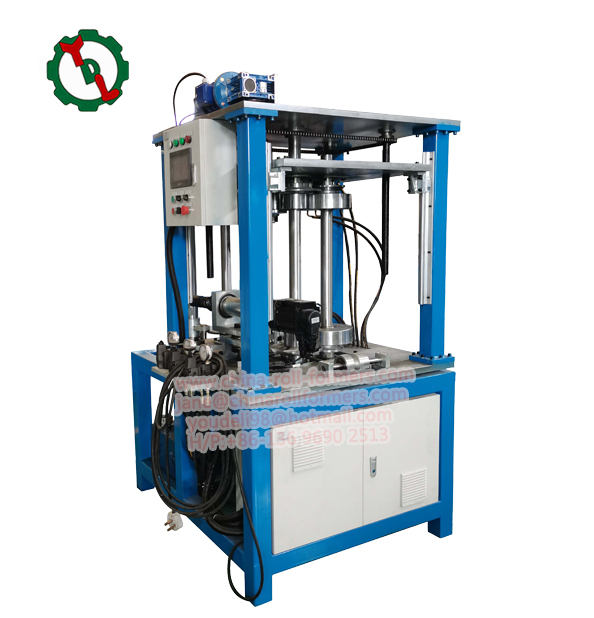
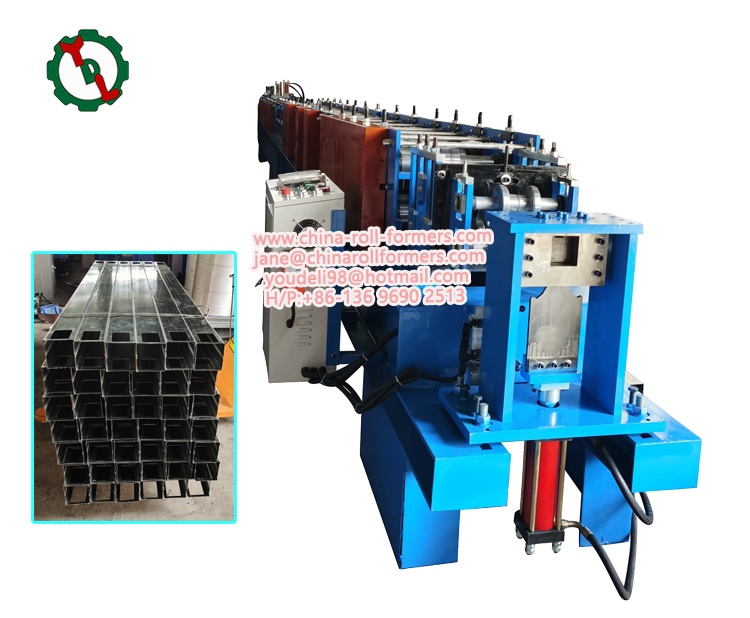
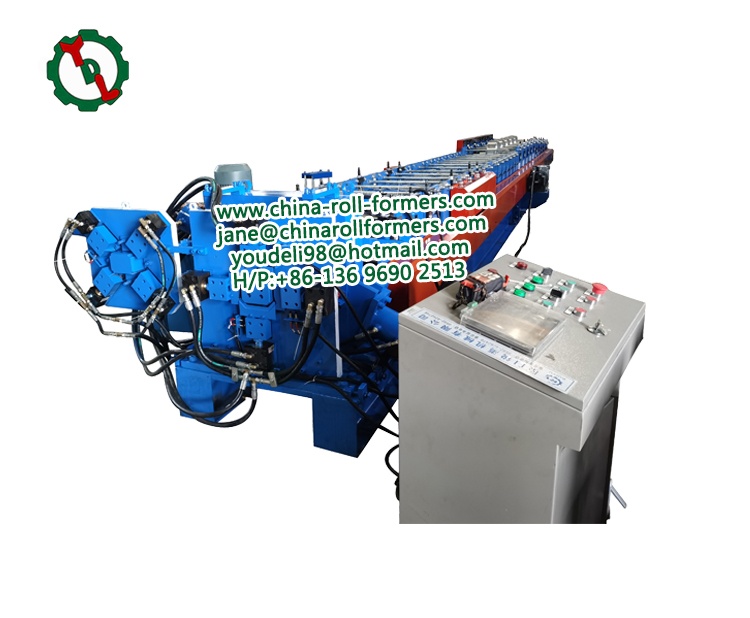
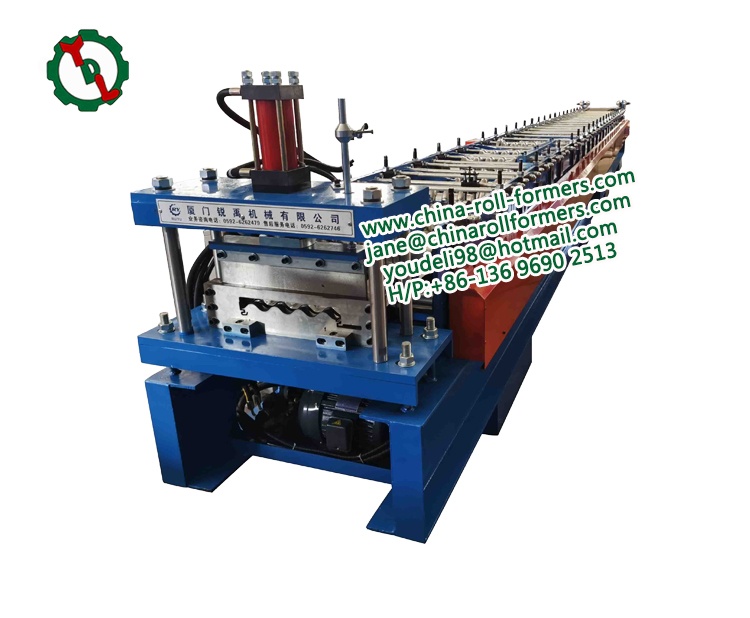
- Roll Forming Station:
Function: The heart of the machine, the roll forming station consists of a series of rollers, each gradually bending the metal into the desired corrugated shape. The number and configuration of rollers determine the final profile of the corrugated sheet. The meticulous arrangement and quantity of these rollers play a pivotal role in defining the ultimate profile of the corrugated sheet, showcasing the intricacy and precision inherent in the corrugated roll forming machine.
- Cutting Mechanism:
Function: Following the corrugation process, the cutting mechanism shapes the continuous sheet into individual segments of the desired length. This step is crucial for producing corrugated sheets of standardized dimensions.
- Control Panel:
Function: The control panel acts as the brain of the machine, housing the electronic components that govern the entire operation. Operators can set parameters such as speed, length, and dimensions through the control panel.
- Stacker:
Function: The stacker collects the finished corrugated sheets, neatly stacking them for convenient handling and transportation. This component enhances overall efficiency by streamlining the end-of-process logistics.
III. Operational Sequence:
- Material Loading:
The process initiates with the loading of the metal coil onto the uncoiler, where it awaits processing.
- Leveling:
The metal coil passes through the leveler, where any flatness variations are corrected, ensuring uniform material quality.
- Feeding and Measurement:
The servo feeder precisely measures and feeds the metal coil into the roll forming station, controlling the length of material to be corrugated.
- Roll Forming:
As the metal passes through the roll forming station, the rollers progressively shape it into the desired corrugated profile.
- Cutting:
The continuous corrugated sheet is then cut into individual segments of the specified length by the cutting mechanism.
- Stacking:
The stacker collects and organizes the finished sheets, preparing them for easy retrieval and transportation.
IV. Precision and Customization:
One of the remarkable aspects of corrugated roll forming machines is their ability to achieve precision and customization. The configuration of the roll forming station, the speed of operation, and the cutting dimensions can be adjusted to meet specific industry standards and client requirements. This adaptability makes corrugating roll forming machines versatile tools in the metalworking arsenal.
V. Applications and Industry Impact:
The corrugated sheets produced by these machines find applications in diverse industries. In construction, they serve as roofing and siding materials, providing durability and aesthetic appeal. The packaging industry utilizes corrugated sheets for creating sturdy and protective containers. Additionally, automotive applications leverage corrugated profiles for various structural components.
- Technological Advancements and Future Trends:
As technology advances, so do corrugated roll forming machines. Modern iterations often incorporate features such as automated controls, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. The integration of Industry 4.0 principles allows for enhanced efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved overall productivity.
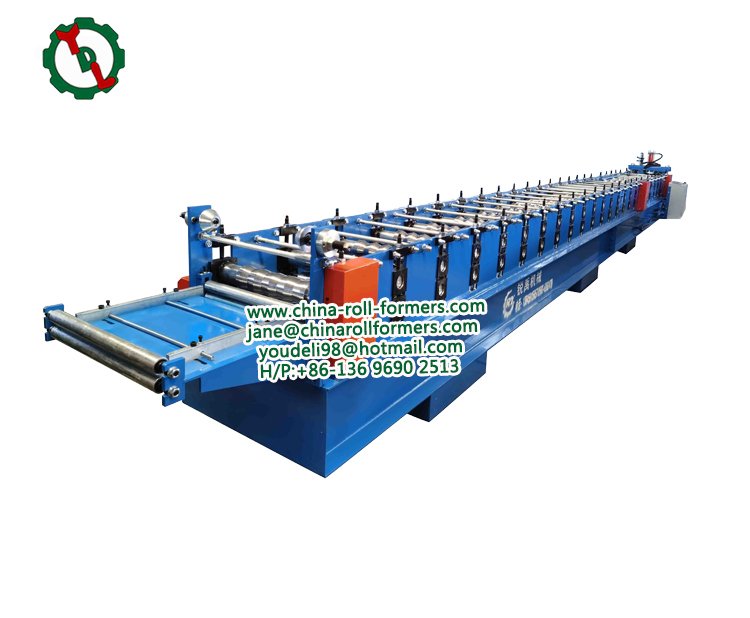

VI. Maintenance and Optimization:
To ensure the sustained efficiency of a corrugated roll forming machine, regular maintenance is paramount. This includes lubrication of moving parts, inspection of rollers for wear, and calibration of measurement systems. Additionally, optimizing the machine for specific materials and profiles involves fine-tuning parameters, such as roll spacing and cutting blade sharpness.
VII. Quality Control Measures:
Quality control is integral throughout the entire process. Advanced sensors and monitoring systems inspect the corrugated sheets for deviations from specified dimensions and surface imperfections. This commitment to quality assurance guarantees that each product leaving the machine meets the stringent standards set by the manufacturer.
VIII. Environmental Considerations:
As sustainability becomes a focal point in manufacturing, corrugated roll forming machines are adapting to eco-friendly practices. Efforts include minimizing material waste during changeovers, optimizing energy consumption, and exploring recyclable materials. These initiatives align with global trends towards greener and more responsible industrial practices.
IX. Training and Skill Requirements:
Operating a corrugated roll forming machine demands a skilled workforce. Operators need to understand the nuances of machine settings, troubleshoot issues, and interpret control panel data. Training programs ensure that operators are adept at handling the intricacies of the machine, contributing to its smooth operation and longevity.
X. Market Dynamics:
The demand for corrugated sheets continues to grow across various industries, influencing the market for corrugated roll forming machines. Manufacturers are responding by developing machines that offer higher throughput, greater customization options, and improved energy efficiency. This competitive landscape underscores the importance of innovation in staying ahead in the market.
XI. Global Reach and Local Impact:
Corrugated roll forming machines are not confined by geographical boundaries. Their impact is felt globally as manufacturers cater to diverse markets with varying requirements. The adaptability of these machines to regional standards and preferences reinforces their role as versatile tools with the potential to shape the infrastructure and packaging landscape worldwide.
XII. Research and Development:
Ongoing research and development initiatives in the field of roll forming technology aim to push the boundaries of what is achievable. Innovations in materials, coatings, and machine design contribute to the evolution of corrugated roll forming machines, ensuring they remain at the forefront of metal processing technology.
XIII. Collaboration and Industry Synergy:
In an era of collaboration, manufacturers of corrugated roll forming machines often work closely with end-users, incorporating feedback and insights into the design and functionality of their machines. This collaborative approach fosters synergy between machine builders and industries, resulting in solutions that precisely meet the evolving needs of the market.
In essence, the operation of a corrugating roll forming machine extends beyond its mechanical aspects. It encompasses a holistic approach, integrating technological advancements, environmental consciousness, skilled labor, market dynamics, and a commitment to quality. This multifaceted perspective is crucial in understanding the machine’s place in the broader industrial landscape.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the corrugated roll forming machine exemplifies the marriage of precision engineering and industrial ingenuity. From the uncoiling of metal coils to the stacking of finished sheets, each component plays a vital role in shaping versatile corrugated profiles. Understanding the mechanics of these machines not only unveils the complexity behind their operation but also highlights their indispensable role in shaping the modern metalworking landscape.